- September 23, 2022
An aluminum cast is a lightweight part made from aluminum material and/or other materials using an aluminum casting process. It is an integral part of industries that desire the durability, strength, and lightweight of aluminum and compatibility with complex product design.
There are several aluminum casting processes, each with a unique setup and requirements. As a result, they are responsible for casting aluminum parts with different properties. This article will introduce aluminum casting and how to choose the right one for your project.
Want to get high-quality cast aluminum parts at competitive prices? Here is WayKen. We offer a wide range of services including die casting, CNC machining, and injection molding to give you cost-effective solutions.

What is Cast Aluminum?
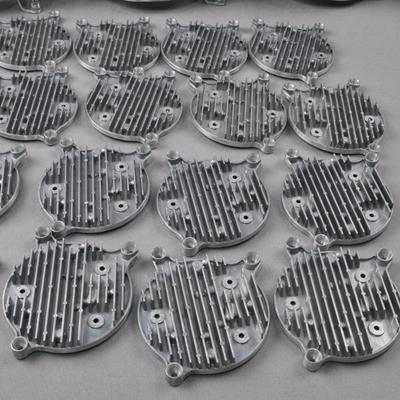
Cast aluminum is a term that denotes a part made from aluminum and/or other metals using one of the various casting processes. Generally, most aluminum casting processes involve heating the aluminum (and other metal) and pouring them in molten form into a prepared mold with the desired product design. Afterward, the molten aluminum cools down, solidifies, and takes the shape of the cavity.
The aluminum cast has the properties of aluminum and the other metals. Furthermore, it develops an external coating of aluminum oxide, which helps to prevent corrosion and it is stronger than the conventional aluminum material.
Cast Aluminum vs Cast Iron
Cast iron looks similar to cast aluminum. However, they are different based on the base material and inherent properties. Below are a few comparisons between both materials:

–Weight: the aluminum cast is lighter than cast iron without losing strength and durability.
–Dimensional tolerance: aluminum cast has a better dimensional tolerance than cast iron due to the softness of the aluminum material in comparison to iron.
–Precision and accuracy: Aluminum is softer than iron which increases the machineability, precision, and accuracy.
–Thermal resistance: Cast aluminum has a higher heat capacity than cast iron. Consequently, it heats up and loses its heat faster than cast iron.
Cast Aluminum vs Wrought Aluminum
Cast aluminum has a higher carbon content than wrought aluminum. Consequently, it is stronger and stronger mechanical properties. Here are the three important differences between both materials.
–Different product forms: On the one hand, wrought aluminum commonly applies to CNC aluminum machining or aluminum extrusion. Hence, they are in a plate or rod form. On the other hand, the aluminum cast has a solid form shaped based on the billet form or into the final product.
–Different alloying elements: Both materials can have the same alloying elements. However, they have different compositions and quantities. For example, aluminum castings have a higher percentage of silicon. Consequently, they have better fluidity.
–Different product properties: Cast iron aluminum is the stronger of the two parts. In contrast, wrought aluminum has higher tensile strength, machinability, and good dimensional accuracy.
Different Aluminum Casting Processes
There are three main metal casting processes suitable for aluminum. Below are the processes and their peculiarities.
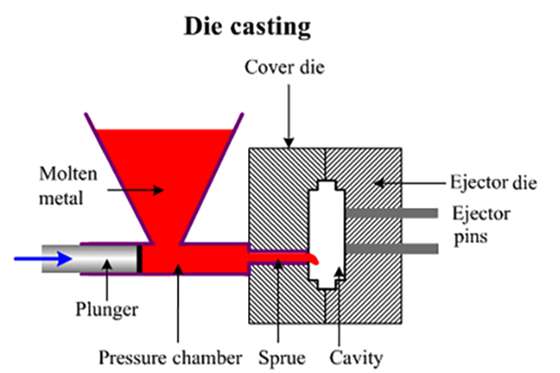
1. Die Casting
Die casting is the most popular aluminum casting process for casting aluminum parts. There are two processes: low-pressure die casting and high-pressure die casting, with the latter being the most suitable for the material.
Die casting involves preheating the aluminum and injecting it under high pressure into a die mold designed according to the intended product. On cooling, the cast aluminum part is removed from the die, and the cycle is repeated after the die cools down.
One of the advantages of die casting is that the die-casted aluminum has excellent electrical and thermal conductivity. Furthermore, they are strong and resistant to corrosion, wear, and heat.
Die-casted aluminum parts are applicable in the mass production of parts in culinary, aerospace, and medical industries.
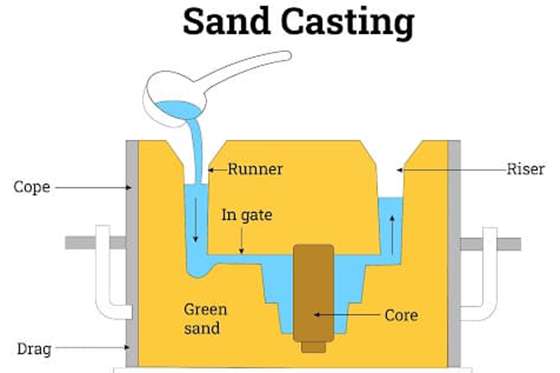
2. Sand Casting
Sand casting is the most common casting process in manufacturing. It is applicable here due to the ability of the sand to withstand elevated temperatures.
The process involves preparing a mold using sand. Afterward, the aluminum material is heated, and the molten aluminum is poured into the sand mold. On cooling, the casted aluminum part is removed.
Sand cast aluminum has low dimensional accuracy and a rough surface finish. Therefore, it most time requires post-processing options such as trimming. The aluminum casting process applies to making aluminum gears, fittings, gas and oil tanks, etc.
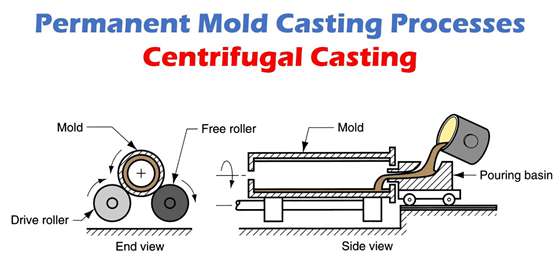
3. Permanent Mold Casting
Permanent mold casting is similar to die casting. However, the difference between the processes is the mechanism of injecting the aluminum into the mold. Unlike die casting, permanent mold casting uses gravity instead of high or low pressure to fill the mold. As a result, it lessens turbulence during the injection process.
Aluminum casts made with this process has stronger with a good surface finish and close dimensional accuracy. The process applies to making aluminum parts in the automotive and aircraft sectors.
How to Choose the Right Aluminum Casting Process?
Each casting process has its advantages and shortcomings. To choose the right process for your project, consider the following factors:

Design Complexity
The design intricacy of the end product influences the choice of the casting process. Large and complicated aluminum casting parts are mostly manufactured using sand casting, which is preferred for products with complicated designs. For dimensionally accurate cast aluminum parts, permanent mold castings are better options.
Speed of Production
Die casting uses a pressurized injection process. Therefore, it is suitable for the mass production of aluminum parts. Sand casting is the next process in terms of speed, with permanent mold casting coming last.
High Quantity
Die casting is the most suitable process for making many aluminum cast parts. However, for balance between high quantity and tooling, sand casting and permanent mold casting are better choices.
Prototyping
Sand casting is the most suitable process for prototyping due to the low investment cost required. The others would require a high investment cost, which is unsuitable because prototyping requires only a few pieces.
Strength and Surface Finishing
Permanent mold casting offers the most advantageous balance of strength and good surface finishing. Nevertheless, sand casting and die casting have comparable strength, with die casting having a better surface finish.
Optional Finishes for Casting Aluminum Parts
Finishing processes can be for aesthetic or functional purposes. Below are a few finishing processes you can consider.
Powder Coating
Powder coating is a dry finishing process that involves the application of dry powder on aluminum. On application, the aluminum cast becomes more durable and has better corrosion resistance.
Painting
This is a popular aesthetic finishing process. However, it can also have a functional purpose. It involves applying a layer of paint to the aluminum part. First, the material is cleaned and sanded. Afterward, a self-etching primer is added, and the layer of paint and an optional extra protective layer containing the enamel sealer. Painting can be a means of color addition or improving the material’s corrosion resistance.
Electroplating
Electroplating involves coating a material with a thin layer of another material. This process works by electrolysis. Using an electrode, pass an electric current through a solution that conducts electricity (electrolyte). For instance, if you want to copper plate the cast aluminum, you need a copper-based electrolyte and a copper anode with the cast aluminum serving as the cathode. The copper from the plating comes from the copper solution, which the copper anode replaces. This process adds aesthetic and protection to the aluminum cast.
Anodizing
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that converts the cast aluminum surface to an anodic oxide finish that is durable and highly corrosion-resistant. It involves immersing the aluminum cast into a tank of sulfur or chromic acid electrolyte (depending on the type) while passing an electric current through the medium.
Advantages of Aluminum Cast
Cast aluminum parts have advantages over other materials. As a result, they are an important part of several industries. Below are a few reasons why you should consider using them.
Fine Surface Finish
They have a smooth and silvery appearance. Therefore, it reduces the need for expensive surface finishing processes. Furthermore, their excellent surface finish makes them applicable in common home products like cookware.
Complex Shapes
The three common industrial aluminum casting processes make it possible to efficiently cast aluminum into any shape. Therefore, it is easier for manufacturers can create parts with complex geometries and accurate dimensions.
Lightweight Parts
Aluminum casts are lightweight without losing their strength, durability, and other mechanical properties. Consequently, they are applicable in making parts that should be light yet strong. For example, the automobile industry extensively uses the aluminum cast to improve fuel efficiency.
Common Applications of Casting Aluminum
Because of its excellent physical and chemical properties, many major industries use cast aluminum. Here are a few common applications of the material.

1. Medical Industry
Medical part manufacturers rely on aluminum casts for their strength and lightweight in making prosthetics, surgical trays, etc. Aside from that, the process is suitable for making complex and accurate shapes which the industry is known for. Also, aluminum is the right material due to its corrosion resistance since much medical equipment comes in contact with body fluids.
2. Automotive industry
Automotive parts manufacturers rely on aluminum casts for their lightweight properties without comprising strength and durability. As a result, it has improved fuel efficiency. Furthermore, making automotive parts with complex shapes with the aluminum casting process is easier. Aluminum casts are suitable for making parts such as brakes and steering wheels.
3. Culinary Industry
Cast aluminum is useful in the culinary industry because of its durability, corrosion resistance, lightweight, and excellent heat conduction. Aside from that, the material is suitable for making cookware because of its excellent heat dissipation, i.e., it can heat up and cools down quickly.
4. Aircraft Industry
Aluminum parts are perfect for the aircraft industry due to their lightweight and strength. Its light weight allows an aircraft to use less fuel to carry more weight.
Conclusion
Aluminum cast are parts made from aluminum and other materials using one of the several casting processes. They are strong, durable, lightweight, and important in industries such as aviation and automotive.
This article introduced aluminum casting, its properties, common aluminum casting processes, and choosing the right process for a project. Are you looking to make accurate parts with cast aluminum? Then let us help you to make products that are strong and of high quality.
FAQ
What is the most accurate aluminum casting method?
The most accurate aluminum casting method is permanent mold casting. Due to gravity, there is better dimensional tolerance and fewer defects compared to die casting and sand casting.
How many types of aluminum casting processes are there?
There are three types of aluminum casting processes. They are permanent mold casting, sand casting, and die casting.
Is die cast aluminum the same as cast aluminum?
Cast aluminum is castings made using casting processes such as permanent mold casting, sand casting, and die casting. However, a die cast aluminum is a cast aluminum made using high pressure die casting.





