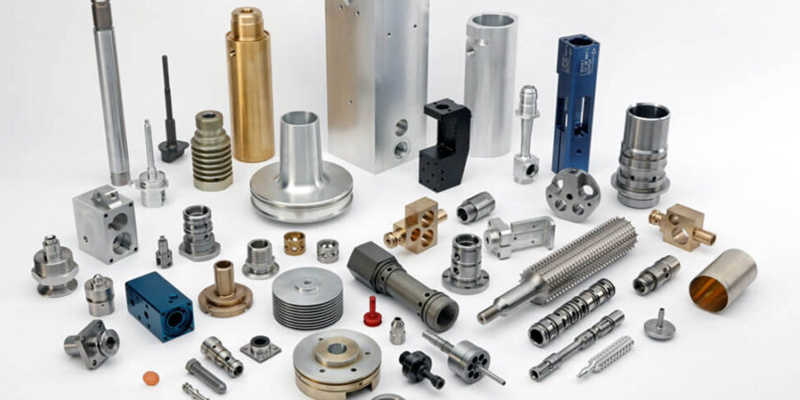
- August 4, 2023
CNC machining has gained much ground in the industrial sector due to its high precision in producing parts and numerous applications in aerospace, medical, automotive, and other industries. Aside from its popularity due to its precision and applications, another reason is its acceptance of working with a wide range of materials.
However, to achieve desired parts that will meet production demands, there are a few important things to consider when selecting material for CNC machining. So, what are the common materials ideal for CNC machining? and are there factors for CNC Machining materials selection? Keep reading.
Different Categories of Material in CNC Machining
CNC machining is a versatile process that allows using several types of materials. These CNC machining materials range from conventional plastic and metals to wood, ceramics, and composites.
In this article, we’d focus more on plastic and metal machining materials as they have more diverse uses across a variety of industries.
Types of Metal Materials for CNC Machining and Examples
The most common material for CNC machined parts is metal. These CNC materials offer numerous advantages, including thermal resistance, hardness, high strength, and electrical conductivity. The common metal CNC machine materials include:
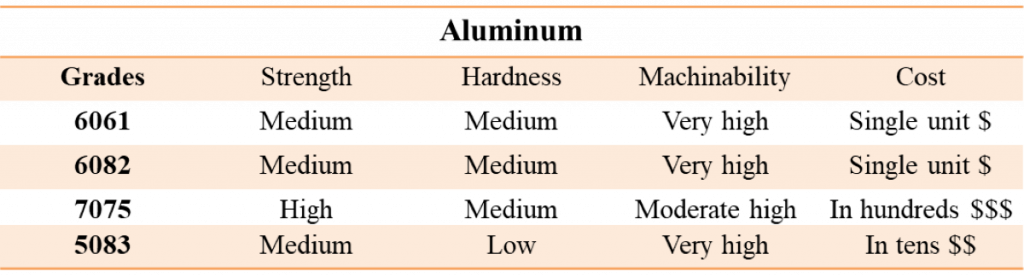
1. Aluminum
In CNC machining, aluminum is one of the most common materials used in CNC machines. It has a high degree of machinability, better than metals like steel and titanium. Also, it boasts a remarkable strength-to-weight ratio, is lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and has an eye-catching silvery aspect.
There are several material grades of aluminum, but not all are ideal for use in CNC machining parts and products. That notwithstanding, aluminum grades like 6061 and 7075 aluminum are highly machinable and often used in the production parts where weight is a consideration, such as automotive engine parts and aerospace frames. These categories of aluminum also find application in consumer electronics, construction, and the medical industry.
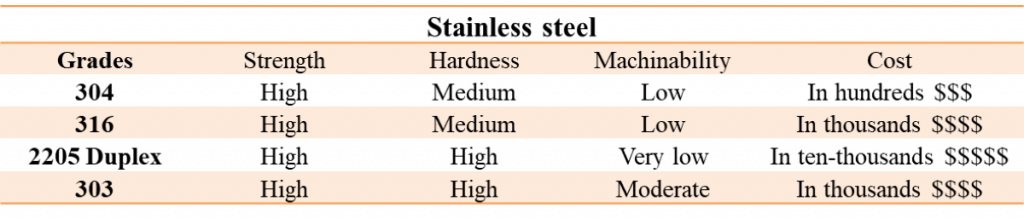
2. Stainless Steel
Stainless steel has great wear resistance, corrosion resistance, strength, and toughness. Like aluminum, this material has a glossy appearance. It comes in different grades and is also often not very expensive. However, its hardness makes it one of the most difficult CNC materials to machine.
316 SS is one of its common grades, and it finds application in outdoor enclosures, medical equipment, and marine applications due to its corrosion and heat resistance. Other common grades of stainless steel for CNC are 303, 304, and 316. They find applications in producing fasteners such as bolts, screws, bushings, etc.

3. Carbon Steel and its Alloys
Due to its superior strength and machinability, carbon steel and related alloys are perfect for various applications. They work well with different heat treatment techniques, which improves their mechanical properties even further. Carbon steel is also reasonably priced compared to other metals used in CNC.
However, it is important to note that carbon steel, mild steel, and its alloys are not intrinsically corrosion-resistant. Besides, their unattractive appearance might not be appropriate for aesthetic applications. Despite their drawbacks, these materials remain favored for numerous industrial and manufacturing applications because of their durability, accessibility, and machinability. Steel and its alloys find application in producing mechanical fasteners and structural components like beams.
4. Copper and its Alloys
Copper is recognized for having great thermal and electrical conductivity. Its outstanding conductivity qualities make it a great choice for electrical and electronic applications, and its malleability and aesthetic appeal make it a popular option in the jewelry sector. Copper finds use in many different industries, including electrical wire, magnetic devices, and jewelry production.
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc known for its corrosion resistance, excellent electrical conductivity, and machinability. It frequently appears in consumer goods, low-strength fasteners, plumbing, and electrical equipment.

Bronze is an alloy of copper, tin, and other elements. It is durable, corrosion-resistant, and strong. Also, bronze has a high degree of machinability, which gives it application in producing gears, bearings, and precision components. In addition, adding phosphorus and aluminum would increase its resistance, improving toughness and strength.
Overall, brass, bronze, and copper are important CNC machining metals.

5. Titanium
Titanium has a high strength-to-weight ratio. In other words, aside from being extremely strong, it is also lightweight. Along with having strong heat conductivity, they are also resistant to corrosion. Furthermore, because titanium is biocompatible, it finds use in the biomedical industry.
What’s more, titanium finds application in producing high-performance machined parts for several industries, including military, aerospace, and medical. Titanium also finds use as a CNC machine tools material.
6. Magnesium
The metal magnesium combines strength and lightweight. It is the best material for high-temperature parts, like engines, because of its superb thermal characteristics. Their lightweight facilitates the production of lighter, fuel-efficient vehicles.
Magnesium machining is renowned for being flammable, can cost more to process, and has a lower corrosion resistance than some other metals, including aluminum.
Types of Plastic Materials for CNC Machining and Examples
Most plastics have low melting points, which consequently hampers their machinability. However, there are some plastics materials for CNC machining, they include:

1. Acrylic
Also known as PMMA (Poly(methyl methacrylate)), this material has several desirable properties, such as optical clarity and rigidity. Its high degree of optical clarity and durability gives it application as a substitute for glass.
Despite drawbacks, including a propensity for cracking and thermal softening, acrylic is still a preferred material for CNC machining because of its adaptability and simplicity. Acrylic is a fantastic material choice for various applications since it can be used to produce accurate, high-quality components.
2. Polypropylene (PP)
High chemical resistance and fatigue strength are the two advantages of adaptable polypropylene. Furthermore, it is a material of medical grade and CNC machining results in a smooth surface finish. One of its drawbacks, though, is that it softens when exposed to high temperatures, making it a little more difficult to machine.
3. Acetal
Also known as POM (Polyoxymethylene) or Delrin, this material is highly versatile. It is tough, as well as resistant to moisture and impact. Furthermore, this material has excellent fatigue resistance.
Acetal’s stiffness, which makes it simple to process with excellent dimensional precision, is one of its main features. As a result, it is frequently used in precision components like bearings, gears, and valves.
Additionally, POM is a dependable material for many industries, including the automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods sectors, because of its superior mechanical qualities and great resistance to environmental conditions.
4. Nylon
Nylon is a strong, durable, and impact-resistant material used in various applications. It has excellent surface lubricating properties and can be employed in several composite forms, such as glass-fiber-reinforced nylon.
Applications that call for protection from frictional forces are particularly well suited for nylon. This includes parts like sprockets, bearings, sliding surfaces, and gears.
5. ABS
Due to its outstanding machinability, tensile strength, impact resistance, and chemical resistance, ABS material is a very affordable plastic material that is suitable for CNC machining. Additionally, it is simple to color, making it perfect for uses where aesthetics is crucial.
ABS has several CNC applications, including creating protective enclosures, rapid prototyping, and creating automotive parts. Aside from CNC machining, ABS manufacturers fabricate ABS using injection molding and 3D printing.
6. UHMW-PE
UHMWPE is a widely used material for CNC machining because of its outstanding qualities, which include high toughness, abrasion and wear resistance, and endurance.
Despite being challenging to machine, UHMWPE is a great material for making sliding surfaces present in bearings, gears, and rollers. Due to its exceptional qualities, it is perfect for applications where great wear resistance and endurance are needed. Compared to other materials, UHMWPE can offer outstanding efficiency and longevity when machined properly.

7. Polycarbonate (PC)
A common plastic used for CNC machining is polycarbonate (PC), which has a certain set of beneficial characteristics like optical clarity. This material is both shatter and heat-resistant. Besides, it can be used in high-temperature applications due to its strong heat resistance. What’s more, polycarbonate finds application in producing electronic components, medical devices, and automotive parts.
8. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK)
PEEK material is a high-performance plastic with excellent chemical resistance. This material also has high dimensional stability and mechanical strength. One of its major advantages is its ability to maintain stiffness at high temperatures, which makes it ideal for use in extreme environments.
PEEK finds application in several industries, including aerospace, food and beverage processing, and oil and gas. It is widely used in producing semiconductor components, bushings, seals, bearings, pump and valve components, etc.
9. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
This is a low-cost plastic material with a high degree of machinability. It is resistant to high impact, corrosion, and chemicals. It has a high strength, which makes it stiff. PVC plastic is ideal for producing welded chemical tanks, valve and pump housings, cabinet and working surfaces, manifolds, and fittings.
Quick View: CNC Machining Material Chart
| Material Type | Name | Grade | Code |
| Metal | Aluminum | Aluminum 1050 | Al 1050 |
| Aluminum 1060 | Al 1060 | ||
| Aluminum 2024 | Al 2024 | ||
| Aluminum 5052-H11 | Al 5052-H11 | ||
| Aluminum 5083 | Al 5083 | ||
| Aluminum 6061 | Al 6061 | ||
| Aluminum 6082 | Al 6082 | ||
| Aluminum 7075 | Al 7075 | ||
| Aluminum-bronze | Al + Br | ||
| Aluminum-MIC-6 | Al MIC-6 | ||
| Aluminum-QC-10 | Al QC-10 | ||
| Brass | Brass | Cu + Zn | |
| Copper | Copper | Cu | |
| Copper-beryllium | Cu + Be | ||
| Copper-chrome | Cu + Cr | ||
| Copper-tungsten | Cu + W | ||
| Magnesium | / | Mg | |
| Magnesium alloy | / | ||
| Phosphor bronze | Cu + Sn + P | ||
| Stainless steel | Stainless-steel 303 | SS 303 | |
| Stainless-steel 304 | SS 304 | ||
| Stainless-steel 316 | SS 316 | ||
| Stainless-steel 410 | SS 410 | ||
| Stainless-steel 431 | SS 431 | ||
| Stainless-steel 440 | SS 440 | ||
| Stainless-steel 630 | SS 630 | ||
| Steel | Low Carbon Steel | 1018 Steel | |
| Medium Carbon Steel | 4130 Steel | ||
| 4140 Steel | |||
| High Carbon Steel | 1095 Spring Steel | ||
| Tin Bronze | / | PVC-white/gray | |
| Titanium | Grade 1 Titanium | Ti grade 1 | |
| Grade 2 Titanium | Ti grade 2 | ||
| Zinc | / | Zn | |
| Plastic | Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene | / | ABS, ABS- high temp, ABS- antistatic |
| Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene + polycarbonate | ABS + PC | ||
| High-density polyethylene | / | HDPE, PEHD | |
| Nylon | Nylon 6 | PA6 | |
| Nylon 6 + 30% Glass Fill | PA6 + 30% GF | ||
| Nylon 6-6 Polyamide | PA66 | ||
| Polybutylene terephthalate | / | PBT | |
| Polycarbonate | Polycarbonate | PC | |
| Polycarbonate-Glass Fill | PC + GF | ||
| Polycarbonate+30% Glass Fill | PC + 30% GF | ||
| Polyether ether ketone | Polyether ether ketone | PEEK | |
| Polyetherimide | Polyetherimide | PEI | |
| Polyetherimide + 30% Glass Fill | Ultem 1000 + 30% GF | ||
| Polyetherimide + Ultem 1000 | PEI + Ultem 1000 | ||
| Polyethylene | / | PE | |
| Polyethylene terephthalate | / | PET | |
| Polymethyl methacrylate-acrylic | / | PMMA-Acrylic | |
| Polyoxymethylene | / | POM | |
| Polyphenylene sulfide | / | PPS | |
| Polyphenylene sulfide + Glass Fill | PPS + GF | ||
| Polytetrafluoroethylene | / | PTFE | |
| Polyvinyl chloride | / | PVC | |
| Polyvinyl chloride + white/grey | PVC-white/gray | ||
| Polyvinylidene fluoride | / | PVDF | |
| Composite | Fiber | Carbon Fiber | CFRP, CRP, CFRTP |
Key Factors for CNC Machining Materials Selection
Although there are usually several factors to consider when choosing the right materials, here are some key ones.
Consider the Requirements for Manufacturing Parts
The basic needs of the parts to be processed are a crucial part of CNC machining, and they also create a guide for the type of material to use. The common part requirements include:

Part Applications
Make sure that the CNC material you intend to use is suitable for the intended application and its environment. For example, let’s examine the comparisons between stainless steel and carbon steel when they want to be used to manufacture components in the marine sector.
Both materials are highly machinable, but stainless steel will be more appropriate since it has a higher level of resistance to corrosion. However, carbon steel will be a better option in a regular, dry environment because it is more durable and stronger.
Part Weight
The weight of the part affects the CNC material selection, as it can impact the machining process and the overall performance of the part. Heavier parts typically require stronger, denser materials to ensure they can withstand the load. For lighter-weight parts, materials with lower density may be used, such as aluminum or titanium, to reduce weight and improve performance.
Part Accuracy and Tolerance
Some materials are more difficult to machine to tight tolerances than others. For example, materials that are prone to warping, such as certain types of plastics (PVC), may require more significant machining allowances to achieve the desired tolerances.
On the other hand, materials such as steel or titanium are often preferred for applications that require high accuracy and tight tolerances.
Part Properties
The properties required for the part depend on its intended use and the environment in which it will be used. Factors such as strength, toughness, and wear resistance are crucial for parts that will be subjected to high stress or wear.
Materials such as steel, titanium, and certain plastics, such as nylon or acetal, are known for their strength and durability, making them suitable for these types of applications. For parts that will be exposed to high temperatures, materials with good thermal stability, such as ceramics or certain metals, may be preferred.
Product Aesthetics
When choosing a material for machining, product aesthetics must be considered. This is because product market acceptance heavily depends on appearance, particularly when it comes to consumer goods.
CNC machinable materials like plastics are available in a wide range of colors and opacity, giving one the leverage to choose between a wide range of material appearances. For metals, on the other hand, improving aesthetics would involve applying a surface finish post-processing.

Surface Finish Options
The surface finish you want your product to have goes a long way in determining the type of material you use for CNC machining. There are different surface finishing options available for metals and plastics, such as polishing, anodizing, passivation, painting, brushing, powder coating, etc. These surface finish options improve not only surface look but also functionality.
It is important to note that these surface finishes interact with materials in different ways. Before choosing a material, confirming its ideal surface finish is best.
Machinability
This entails how easily machinable a material is. Softer materials like plastic and metals like aluminum are quite easy to machine. However, with tougher materials like carbon fiber and titanium, machining is a tad more difficult because these materials often destroy cutting tools. Making parts using materials with a high degree of machinability saves long-term time and money.
Cost
Of course, every material for use in CNC machining has a consideration cost. However, we firmly advise all product designers to consider that picking a lower grade of material to save money is never a smart move over the long haul.
Choose the high-quality material you can purchase that provides all the required capabilities. Only doing so increases the finished parts’ durability.
Tips When Using CNC Processes to Machine Different Materials
What you’re trying to manufacture ultimately determines which CNC machining materials to employ for your parts production. However, the following tips might serve as a quick CNC materials guide.
Use Quality Tooling
Regardless of the material you want to machine, it is important to use high-quality tooling. By avoiding inexpensive cutters that readily break and soon wear out, you can save yourself some money and headaches. High-quality tooling is designed to withstand the rigors of high-speed machining, improving the quality and consistency of your output.

Install Reliable Work-holding on Your Machine
Although maintaining a part in place is crucial during machining, sometimes it is easier said than done. This is even more difficult when working with delicate materials and complex shapes. Hence, it is better to install reliable work-holding on your CNC machine for improved machining precision and accuracy.
Select Common Machining Materials
Instead of worrying about choosing from the myriad of materials available, you can select common machining materials which top rated engineers identified and conclude that it works well for machining and is widely accepted for such applications.
Common metals include brass, copper, stainless steel, and aluminum. Common plastics include PEEK, Acetal, Nylon, ABS, and Polycarbonate.
Get the Right CNC Machining Material for Your Projects
If you are struggling to choose the right CNC materials for your projects, WayKen is here to help you. We can provide 60+ engineering metals and plastics and have well-experienced machinists and engineers who help recommend materials for your project within your budget range.
Furthermore, with our one-stop CNC machining services to meet your expectations, you can confidently get prototypes and parts with high quality and accuracy. Have any specific questions about material machining, please feel free to contact us.
Conclusion
A CNC machine’s ability to work with diverse materials is one reason it remains one of the best manufacturing processes. It easily facilitates the production of parts using metal, plastic, wood, and composite materials. Before choosing a material for your part, it is best to research the material’s strengths, weaknesses, as well as other properties to make the right decisions.
FAQs
What are the factors to be considered when selecting a CNC material?
It would be best if you considered many factors, including environmental, uses, machinability, tolerances, and the cost of the material.
Which aluminum alloy is the best for CNC machining?
Aluminum 6061-T6 is a commonly used aluminum alloy, and it is known to be a standard grade for CNC machining. Its properties, like lightness in weight, resistance to corrosion, versatility, and machinability, make it applicable in the automobile and aerospace industries.
Which plastics are more machinability?
Acetal, PEEK, and PVC plastic materials offer good dimensional stability, excellent machining properties, and resistance to melting and chipping. Due to its low price and superior machinability, Delrin is also regarded as the most economical plastic.
What is the hardest metal to mill?
Titanium is infamous for being one of the hardest metals to machine, and there are numerous stories of wrecked workpieces and shattered tools. However, titanium has outstanding qualities that make it a frequently utilized material in the aerospace and medical industries.






