Posted on: July 13, 2018, | By Will, WayKen Project Manager
With the development of technology 3D printing has evolved into reality from a mere concept. The saturation of industries made the main aim of the manufacturer not only to manufacture products but also to use innovative methods in order to produce more products in the shorter span of time to increase the production. So the manufacturers these days are using different rapid prototyping techniques. These innovative methods not only save time but are also cost-effective. One such rapid prototyping technique being employed these days is the use of 3D printing (SLA prototyping & SLS prototyping). 3D printing, in addition to saving time and cost, also produces the best functional prototype from a 3D CAD model of the product.
History of 3D Printing
The concept of 3D printing is as old as 1981 when Nagoya Municipal Industrial Research Institute utilized photo-hardening thermoset polymers in order to fabricate the three-dimensional models where a mask pattern was used to control the UV exposure area. But at that time its use was less due to the restriction of materials and 3D modeling software. As early as 2000, China had imported commercial rapid prototyping equipment, among the main application was industrial 3D printing. It became a popular word in the industrial world in 2013 when two NASA employees Samantha Snabes and Matthew Fiedler introduced the first prototype of an affordable 3D printer, Gigabot.
3D Printing: A Leading Trend in Rapid Prototyping
From reducing costs to increase efficiency with the innovation, many people are excited about the impact that 3D printing will have on the future of manufacturing. However, the truth is, it already has made a significant impact on the industry as well as domestic customers.
A domestic 3D printer is used as an R&D product and to design the 3D models in the industries. But it is wrong to say that it is only a product for industrial customers. It is now becoming widely popular among civilian customers due to its large applications. Mainly it is because the material used in 3D printing is becoming cheaper and readily available with the passage of time. Furthermore, 3D printer occupies much lesser space as compared to conventional subtractive tool room methods such as CNC milling, lathe, and precision grinding.
The availability of the modeling software nowadays is also aiding towards the development of this technology. Generally, the model is saved in STL format which is a CAD file format for rapid prototyping that stores data based on triangulations of CAD models. But this format used to save the file in a large number of lattice structures which produces errors. But the newer software stores the file in Additive Manufacturing File Format (AMF) that produces a lesser number of errors. Moreover, these software’s have a user-friendly interface which makes it easy for the domestic as well as industrial users to model a 3D model of the product.
A recent study showed that 6.7 million 3D printers will be shipped worldwide by 2020 which is 14 times more than in 2016. As new technologies improve the uses of 3D printers, the technology will continue to bring the manufacturing industry to greater heights of glory
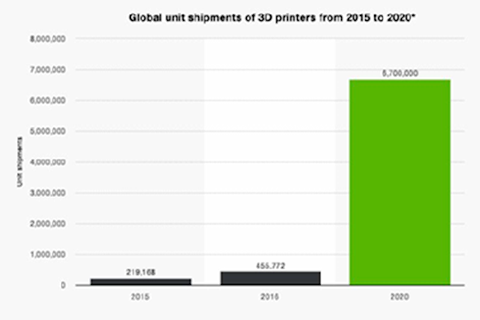
Figure 1: Global unit shipments of 3D printers from 2015-2020
3D Printing Technology
When it comes to 3D printing technology, there are two most commonly used technologies: SLA Rapid Prototyping & SLS rapid prototyping.
1. SLA Rapid Prototyping
SLA rapid prototyping also known as Stereolithography is a type of 3D printing technology that is used to create different prototypes, models, patterns in layer by layer fashion using the technique of Photopolymerization. Photopolymerization is a process of molecules linking to form polymers under the action of light. So basically the resin (material used in creating the prototype) is solidified using the light and ultraviolet rays. In this way, the desired prototype is created layer by layer using SLA rapid prototyping.
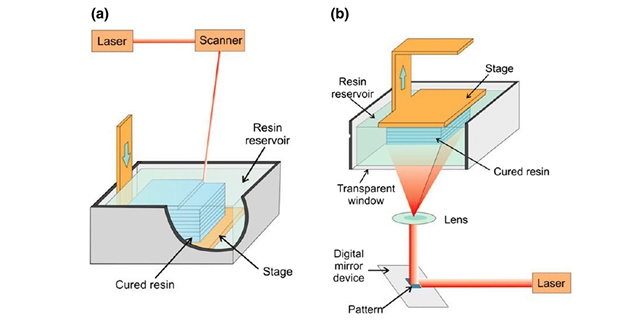
Figure 2: A figure showing the processes of SLA rapid prototyping
The UV radiations are used to build a pre-programmed shape on the photopolymer vat. As the photopolymers are sensitive to UV radiations, therefore, the resin in solidified and forms a single layer of the desired prototype. In this way, layers of resins are solidified until the desired prototype is formed.
SLA prototyped products have the highest resolution and surface finishing of all the 3D rapid prototyping techniques but its versatility lies in the resin used. With the development of technology, material engineers have created different resin used in SLA prototyping with properties matching those of standard engineering thermoplastic materials.
Uses
SLA rapid prototyping is widely used in different industries for the development of products since its inception.
· Medical Modeling
SLA rapid prototyped products are being used in medicine since the technology was introduced. It is used to create anatomical 3D models of different regions of a patient’s body on the basis of data obtained from computer scans. These models are then used in aiding of diagnosis and treatment. Surgeons use these models as they assist them in surgery while the Prosthetists use them to manufacture custom fitting implants.

Figure 3: A model produced by SLA rapid prototyping
· Prototyping
SLA rapid prototyping is also used to create the prototypes of even/irregular shaped materials at relatively lower cost. Prototypes made up by SLA rapid prototyping method are capable of being machined and patterns of various metal casting operations can be formed.
2. SLS Rapid Prototyping
Selective Laser Sintering commonly called SLS rapid prototyping technique uses the laser as a solidifier for the powdered material. Mostly the powdered material used is nylon. Nylon is an engineering thermoplastic with impressive mechanical properties and is lightweight and stable. This type of 3D printer automatically aims the laser at the powdered material causing it to solidify in order to create the required structure. SLS rapid prototyping is different from Selective Laser Melting as in SLM. The material is melted rather than being sintered as in SLS rapid prototyping.
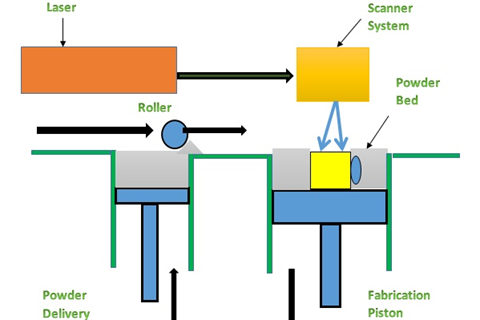
Figure 4: A figure showing the processes of SLS rapid prototyping
SLS rapid prototyping, like SLA rapid prototyping, uses the computer-aided designs in order to develop the required prototype with the help of sintered powder. It uses high power laser mostly carbon dioxide laser which is a source of fusion of small particles in the form of powder to form the required prototype. The laser scans the cross sections that are generated by the cad model and selectively fuses the sintered materials in the shape of a required prototype. After the cross-section is scanned the powder bed is lowered and a new layer of material is applied on the top until the desired product is formed.
The nylon material used in SLS rapid prototyping makes it useful for creating prototypes of high mechanical strength as well as impact, light, and water resistant prototypes. Lower cost production and high productivity make this technique quite popular among the industries for rapid prototyping.
Uses
SLS rapid prototyping is widely used in different industries for the development of products since its inception
· Aerospace Industry
SLS rapid prototyping is quite popular among industries where high-quality parts are required in lesser quantities. One such industry is the aerospace industry where prototypes for aircraft are required. As aircraft and other aerospace vehicles are built in lesser number and remain in service for decades so SLS rapid prototyping is used to produce high-quality parts for the aircraft industry.

Figure 5: A compartment panel produced by Airbus by using SLS rapid prototyping
· Prototyping of Complex Geometries
SLS rapid prototyping is widely used in the industries to produce geometries with complex shapes by using their CAD model. It is because SLS rapid prototyping can produce prototypes with a variety of materials causing them to fuse under the action of the laser. No need to support structures also makes it widely popular among the industries producing parts of higher quality.

Figure 6: A propeller designed by SLS rapid prototyping
Comparison between SLA and SLS
1. Raw Material Used
SLS -The raw material used varies from Nylon Powder; Polycarbonated carbon powder to Vinyl chloride; Powder but with high performance.
SLA -The raw material used is a liquid polymer with not quality comparable to that of thermoplastic materials.
2. Material Shrinkage
SLS -Material shrinkage ranges from 2-4%.
SLA -Material shrinkage is lower than 0.4%, so more detailed parts can be produced.
3. Build Size
SLS -Prototypes of size up to 1500 x 750 x 500 mm can be produced.
SLA -Prototypes of size up to 145 x 145 x 175 mm can be produced.
4. Surface Finish
SLS -The finish of the material is rough and somewhat loose.
SLA -The finish of the material is relatively smooth.
5. Strength
SLS -The strength of the produced parts is high due to the raw material used.
SLA -The strength of the material produced is relatively low.
6. Machining Operation
SLS -The produced prototypes are easy to be machined such as milling, lathe, drilling etc.
SLA -The strength of the prototype is low so machining is difficult and great care should be taken.
7. Resistance to Wear and Tear
SLS -Resistance to wear and tear is similar to that of thermoplastic materials.
SLA -Poor resistance to environmental conditions. Use of epoxy resins can considerably improve the resistance.
Figure 7: A Model produced by SLS rapid prototyping
Benefits: 3D Printing using SLA and SLS
In order to mass produce the products within a shorter period of time, 3D printing is an essential tool. There are many benefits that can be enjoyed by employing this technique.
1. Cost Effectiveness
Cost-effectiveness is one of the main benefits of 3D printing. The strength and finish in the prototype produced from this process don’t want any modifications which save money. Moreover, the products can be mass produced which also saves a lot of money.
2. Speed
This technique enables the industrialists to produce a greater number of products at higher speed consuming much lesser time as compared to conventional industrial processes used. The user only requires a CAD model and the printer uses that model and develops the product at a much less time. Moreover, the designed prototype is of high quality and strength making this technique popular in industries as well as civilians all around the world.
3. Reduction of Storage Space
3D printer consumes much lesser space as compared to conventional mass production machinery being employed by the industries till now. Moreover, the tools of those machines are heavy and expensive as compared to a compact 3D printer which consumes much lesser space.
4. Mitigation of Risk
3D printing also enables the verification of a design before the production of an expensive prototype in the CAD model. So the CAD model has corrected accordingly. Moreover, the production of test molds is far cheaper than altering an already produced mold.
5. Feedback
With a prototype, one can test the market potential of the product before actually producing it. The response of the buyers before actually producing the product can predict the future prospect of the product and can help in deciding the number of the products to be mass produced in order to be supplied to the market.
6. Personalization
With the standard machining operations being used for the mass production, all parts come off the machine or the mold with the same design or defects if any. But in the case of 3D printing, there is always roam of customization, personalization of the product as per required by the customer or the market demands.
Concluding Remarks
Both SLA prototyping and SLS prototyping are considered one of the great revolutions in the technological world. Production of a functional prototype is now no more a difficult task because it can be easily produced by the employment of these two techniques as per requirement of the characteristics of the prototype. SLA is better for surface finishing but SLS is better for production of high strength products. Both are top of line rapid prototyping techniques and can be used for the mass production of products with fewer errors in them.