Prototyping for Design & Engineering Validation
Transition the product development process from engineering prototype to engineering validation, design verification, and production verification.
- Home
- Applications
- Design & Engineering Verification
What is Engineering Prototype
Use Engineering Prototypes to Ensure Design for Manufacturability
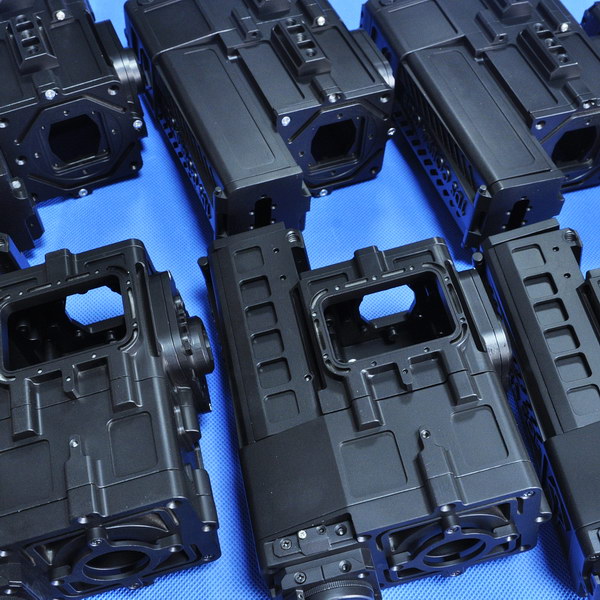
During product development phases, product validation testing procedures become paramount to provide test and analysis results. First, building an engineering prototype is essential. It is a series of components created by combining engineering and design to represent the end product. Such powerful and high-precision pilot production prototypes often manufactured using rapid prototyping undergo rigorous test and evaluation to validate product design, engineering, and manufacturability.
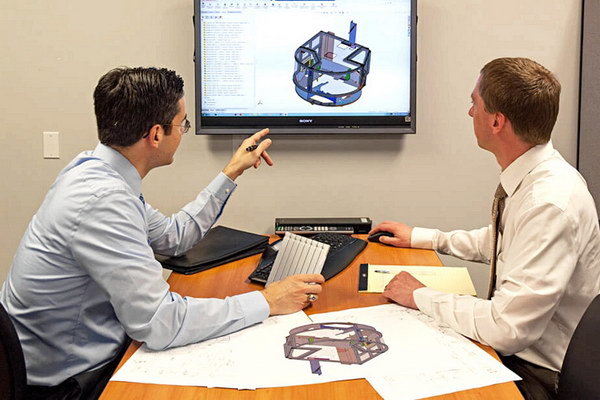
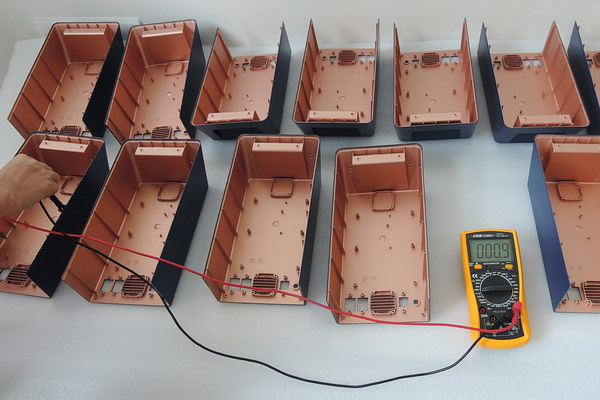


Why Validation and Testing
Prototype Engineering Focuses on Optimizing Mass Production
As product development moves into subsequent phases when design and engineering meet, engineering prototyping and testing help identify problems. Identifying improvements and iterating before investing in expensive tools and putting them into production makes the future production process as smooth and reliable as possible.
The design can be verified to meet the expected product specifications and performance through a series of verification test processes, including basic functional testing, manufacturing processes, performance parametric measurements and certification standards verification. The goal is to verify that the design has been properly implemented into production.
Choose the Right Prototype Partner for Your Design & Engineering Validation
- An engineering team with expertise in varying manufacturing processes.
- Provides test parts similar to end-use products using CNC precision machining, rapid tooling, and injection moulding techniques.
- Assisting with CAD design reviews to ensure compliance with predetermined production requirements before prototyping or manufacturing.
- Solving engineering challenges by providing advice on the best component design based on material, process, and accuracy requirements.
- Anticipate potential production problems and optimize solutions quickly, saving time and money.
How to Test in 3 Different Engineering Validation Stages
Verification is a progressively rigorous process that combines design and engineering development alongside prototyping and manufacturing and is designed to provide objective, comprehensive testing to meet the product’s intended design requirements, performance, specifications and standards, and to ensure that mass production can be sustained.
Engineering Verification Tests (EVT)
EVT verifies product compliance with a design specification functional requirements. EVT versions stem from CNC machining, vacuum casting, or rapid tooling.
- Quantities range from 20-50 pieces
- Material and mechanical properties of parts must meet testing requirements
- Tighter tolerances are required to verify assembly and in-use functionality
- Basic performance testing, including power, thermal, and EMI
- Identify design or process defects
- Determine design or process improvement options
- A second EVT is performed after making changes
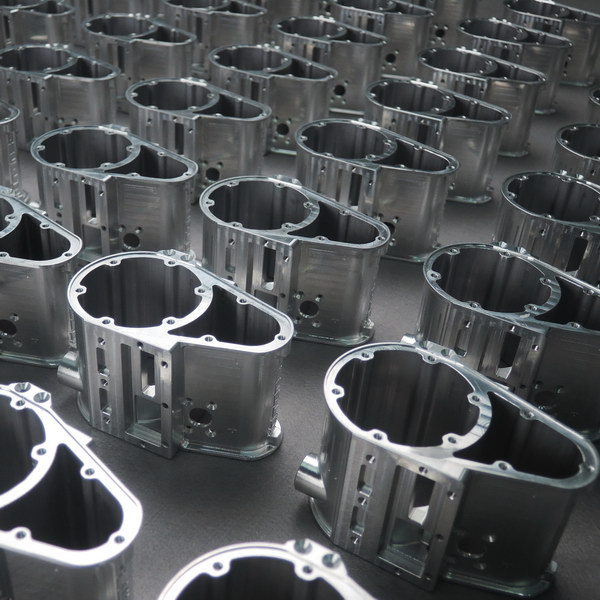
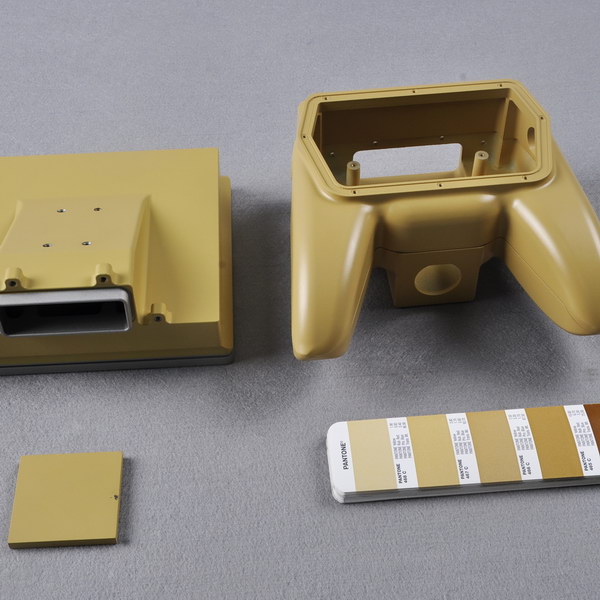

Design Validation Testing (DVT)
DVT is an intensive series of test procedures that verify product compliance with specifications, industry standards, and certifications. It also refines tools and processes for consistent production runs, while using pre-production components to meet ideal testing requirements.
- Quantities typically range from 50-200 pieces.
- All parts should come from a mould or pre-production process.
- Ensure production process meets chemical and environmental requirements.
- Extensive reliability and compliance testing, including flame retardant, drop, waterproof, battery safety, etc.
- Verification of product certifications and standards in different countries or regions, like RoHS, CE, FCC, UL, etc.
- Need for rapid failure analysis and corrective action.
- Optimization of production schedules.
Production Validation Testing (PVT)
PVT is the first trial production run to identify flaws during each production line stage and evaluate optimization. The entire production line undergoes testing to ensure quality assurance.
- Product quantity often exceeds 500 and are ideal for sale.
- Tooling commences without changes.
- Mass production validation (yield, time, target cost, rework time, etc.)
- Design for Assembly (DFA) validation to optimize the assembly process and reduce time and cost.
- Development and testing of Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) procedures.
- Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) development and employee training procedures.






