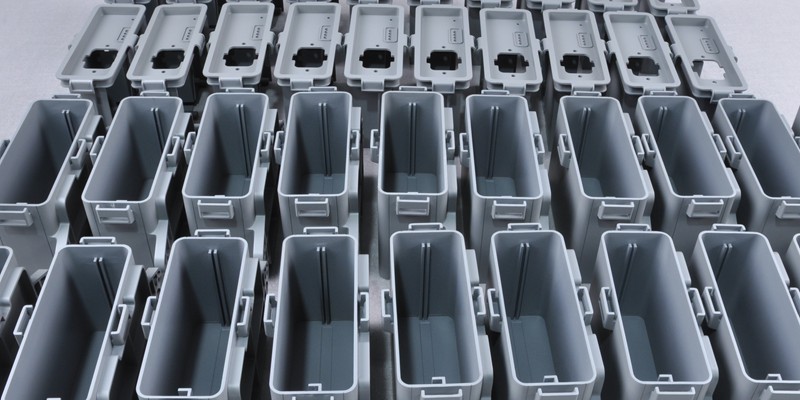
- April 12, 2024
Vacuum casting is a crucial process in the creation of plastic parts. It is a useful technique for making small quantities of polyurethane parts because of its effectiveness and speed. This method is very useful for producing prototypes of a product, which enables producers to evaluate the market before beginning large-scale manufacturing.
The purpose of this article is to answer the question: what is vacuum casting? we will explore all aspects of the urethane and silicone casting process, covering its uses, the materials utilized, and the advantages and limitations.
What is Vacuum Casting or Urethane Casting?
Vacuum casting or urethane casting is a process that involves pouring urethane resin into a space between two silicone mold halves. Using a vacuum chamber to extract air from the mold during the vacuum casting technique helps guarantee that the object takes on the correct shape.
This vacuum casting technique is often used to make rubber and plastic items. Since urethane molding can be quicker and less expensive than other techniques like injection molding, it often finds use in prototyping projects or small-scale production runs. The procedure creates high-quality, bubble-free castings with a flawless, smoothly textured surface since it is done under vacuum.
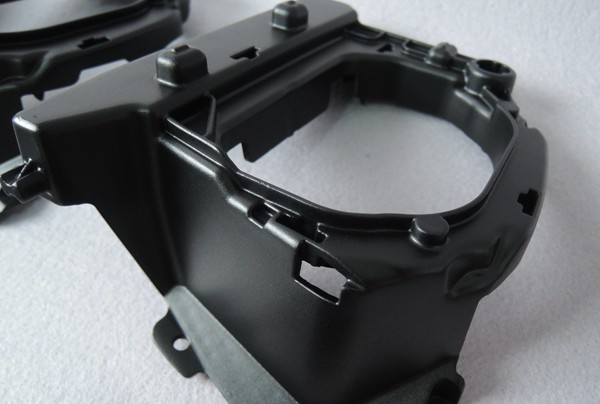

Therefore, vacuum casting’s primary benefit is its high accuracy and repeatability, which makes it an ideal option for small-batch plastic parts requiring exact dimensions. It also makes it possible to cast more complex designs. Nonetheless, it is important to note that vacuum casting isn’t appropriate for every application, especially true for materials that are heat and pressure-sensitive.
Vacuum Casting Process: Step by Step
In order to operate, vacuum casting needs a mold tool having a cavity in the shape of the part, just like conventional injection molding. Here we break down the vacuum casting process step by step.
Step 1: Make a 3D Model of the Part
To begin with, it is necessary to secure a high-quality master model with excellent dimensional accuracy. To obtain the appropriate surface texture and quality, this master model is usually created using 3D printing or CNC machining. The final vacuum-casted part will retain every little feature exactly as it is, therefore making a perfect master model is crucial.

Step 2: Create the Silicone Mold
The next step is building the silicone mold using the master plan created in step one. Here is how to build the silicone mold:
- Inside the casting box, suspend the master model and equip it with cores, inserts, and casting gates. Also, fasten risers to the component to let the air out of the silicone mold.
- After that, pump silicone into the casting box and around the master model under a vacuum, capturing each detail.
- Allow the silicone to cure inside an oven for 8-16 hours at a temperature of 40°C. The exact time will depend on the size of the silicone mold.
- After curing and drying the silicone rubber, remove the box and risers. Then, split the mold carefully using a knife to expose the negative shape cavity of the part.
To ensure that the mold surface is non-sticky and free from defects, please use the right mold-release agent.
Step 3: Mix the Polyurethane Resin
Before using polyurethane resins for vacuum casting, it is important to first heat it to a temperature of 40°C before mixing. Subsequently, mix a two-component casting resin, incorporating any desired color, and transfer the mix into the machine’s bowl. After that, attach the pouring gates to the mixing and pouring bowls and put the mold back in place.
Mix the casting resins and color pigment and allow to deaerate under vacuum for 50–60 seconds during the auto-pouring process. In order to prevent any voids or air pockets, pour the resin into the mold while vacuuming it. Vacuum guarantees mold-free bubbles and eliminates flow resistance brought on by air pockets inside the tool. Gravity feeding is ideal for filling the mold.
![]()
Step 4: Remove the Cast Part from the Mold
After casting the resin, the final stages include oven-curing to enhance the material properties of the item, trimming the edges of flash material, and another polishing cycle using different sandpaper according to requirements.
As the number of castings increases, the silicone mold will gradually lose its shape if it exceeds these limits, which will impact dimensional accuracy.
Guidelines for Effective Design in Vacuum Casting
These guidelines will help you critically modify features during the design phase and create accurate vacuum casting products.
Wall Thickness
Vacuum casting allows us the ability to include different wall thicknesses in a single part. To ensure structural integrity and achieve the optimum outcomes, it is best to keep wall thickness consistent and suggest 1.5mm thick.
Tolerances
Tolerance design ensures your parts fit together and fulfill the required standards. A 0.15% shrinkage occurs during silicone mold casting. Consequently, it is important to consider this shrinkage when making parts.
Ribs
For large flat sections, in particular, adding ribs increases strength and decreases warping. Also, note that to stop the ribs from shrinking and sinking, their thickness must be smaller than that of the nearby walls. Rib thickness should ideally be a minimum of 60% of the nominal wall thickness.
Bosses
Bosses are frequently used for designing housings or casings. At attachment locations, they increase strength. They should be at least 1 mm in height and diameter. It is also important to make sure that their wall thickness does not go above 60% of the nominal part thickness to reduce the chance of them sinking.
Undercuts
Vacuum casting undercuts do not require inserts and can be designed freely, in contrast to methods that call for hard tooling.
Embossed Details
To maintain clarity and visibility, texts and logos that are embossed (raised) or debossed (recessed) should have a minimum depth or height of 1 mm and a minimum width of 1 mm. To improve readability, keep a 1mm space between characters as well.

Different Materials for Silicone Molding and Vacuum Casting
There are various materials used in silicone molding and vacuum casting, each chosen based on the properties required for the final product.
Silicone Mold Materials
Tin-cure and platinum-cure silicones are the two categories into which casting silicones fall. Tin-cure silicones, also known as condensation-cure silicones, exhibit shrinkage of 1-4 percent. While model manufacturers will make every effort to account for shrink rate, it is preferable to use higher-quality platinum-cure silicone or high-temperature vulcanization (HTV) rubbers for high-tolerance applications.
In addition, an A 40-50 Shore hardness will result in a mold that is long-lasting and easily demolding, even for pieces that would become stuck in a rigid mold due to undercuts. Using a translucent silicone is also advised as it makes air traps, bubbles, impurities, and other interior mold elements visible.
Vacuum Casting Materials
There are numerous vacuum casting materials exist, each with a unique combination of stiffness, elasticity, hardness, and flexibility.
- General-purpose resin similar to ABS;
- Glass-filled nylon-like substance for increased stiffness;
- TPE-like elastomeric material for use in wearables, buttons, hand grips, gaskets, and sealing;
- Polycarbonate-like materials;
- Water-clear or translucent casting urethane (similar to PMMA);
- Heat-resistant materials that resemble PU or POM.
A few unusual urethane casting materials are also available, including food-grade, conductive, low-density, and fire-retardant alternatives, as well as materials that mimic shatter glass, wax, epoxy, ceramic, and composites.
Options for Surface Finishing in Vacuum Casting
The molding process offers a multitude of options for surface finish, including
- Vacuum Metalizing
- Vapor Polishing
- Silk screening/pad printing
- Painting
Applications of Vacuum Casting in Various Industries
Vacuum casting technology is adaptable and has numerous uses across various sectors. This method is an ideal option for high-quality output because it can produce complex and accurate components. Here are applications of vacuum casting as used by different industries.

Automotive Industry
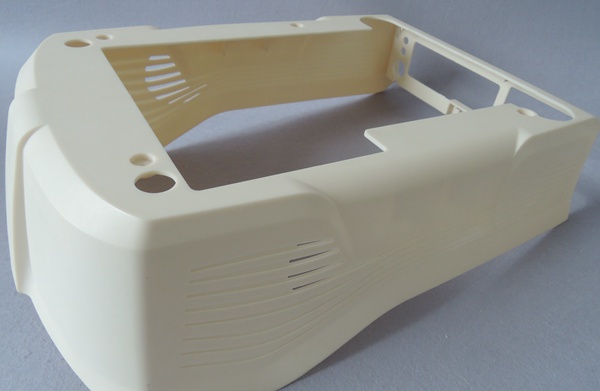
The automotive industry benefits greatly from vacuum casting. It ensures total insulation and protection of car components, such as coils, sensors, rotors, and stators, among others. It is also extensively utilized for low-volume manufacturing and prototyping. Vacuum-casted elements, like engine covers, dashboards, and handles.
Medical Industry
The medical industry demands high-quality batch production and rapid prototyping, and vacuum casting delivers both. Dental implants, medical equipment prototypes, and personalized prosthetics can made using vacuum casting, ensuring that prostheses are made with exact weights, sizes, and symmetrical proportions
Aerospace Industry
Precision parts for aircraft can be made with this technology. Vacuum casting is frequently used to manufacture precise details and achieve greater accuracy in components like fuel systems, air ducts, and even some exterior elements of airplanes.
Consumer Goods Industry
The consumer products industry utilizes vacuum casting to manufacture limited quantities of everyday items such as packaging, accessories, household appliances, baby toys, and electronics. While the final products for these items are made using injection molding, vacuum casting is useful to used to create prototype product for verification and testing.
Key Technical Specification for Vacuum Casting
- Material Choice: A wide range of material selections is available including rubber, resin, and plastic;
- Maximum Part Dimension: The dimensions of the vacuum chamber restrict the size of the mold;
- Minimum Wall Thickness: The wall of the mold must be at least 0.75 mm thick in order to guarantee correct filling. However, the recommended wall thickness of 1.5 mm yields the optimum performance;
- Surface Texture: Shiny, matte, textured, and polished finishes
Advantages and Limitations of Vacuum Casting Process
Examine these benefits and drawbacks of the process to determine if the vacuum casting method is right for your intended applications:
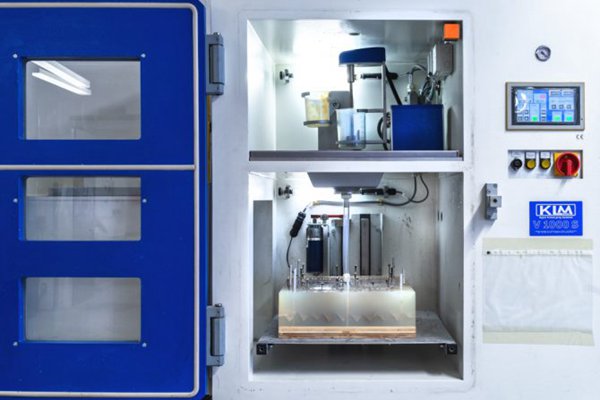

Advantages
- One benefit of the vacuum casting method is the ability to produce pieces with intricate features. The 3D printed or CNC machined master model is used to build the silicone mold and then mirrored in the finished cast.
- Parts made by vacuum casting have exceptional dimensional accuracy. The components made by vacuum casting will fit together flawlessly.
- The process’s essential equipment, silicone molds, is comparatively less expensive to build than metallic molds. While silicone molds can be made for a few hundred dollars, injection molding may cost thousands of dollars.
- Vacuum casting has a very quick lead time as the process takes less than 15 days from start to finish.
Limitations
- The silicone molding process works best with polyurethane resins and elastomers, but it’s not suitable for molding hard industrial materials, for instance, metals. For metal casting, there’s a specialized similar process called vacuum die or die casting.
- These silicone molds don’t last very long. They can produce twenty to twenty-five high-quality pieces before the level of intricacy and precision starts to decline.
- Because the surface finish is dependent on the post-processing of the part, it is occasionally restricted to the outside since certain internal pattern features are hard to access.
Comparing Vacuum Casting to Other Manufacturing Processes
Not sure which plastic manufacturing process to use? Let us now compare vacuum casting to both injection molding and 3D printing to help you make the right production decision.
Vacuum Casting vs Injection Molding
In the case of vacuum casting vs injection molding, injection molding produces items by applying intense pressure to molten material inside a metal mold. Although it takes longer to make than silicone molds used in vacuum casting, it is perfect for high-volume production.
Nonetheless, the initial expenses of tooling are much greater. Conversely, silicone molds are used in vacuum casting. With less money, upfront for creating molds, it offers flexibility in design modifications.
Vacuum Casting vs 3D Printing
Using a digital file as a starting point, 3D printing is an additive manufacturing technique that manufactures items layer by layer. This implies that it supports any form of complicated and intricate geometry that can be created digitally. Although it can create pieces rather fast and with great adaptability, creating many duplicates takes time, increasing 3D printing service costs.
On the other hand, vacuum casting does take a little longer because it requires a high-quality master model. However, it is faster to create several copies of a part with uniform surface finishes and material qualities once a mold has been created.
WayKen: Your Reliable Manufacturer for Vacuum Casting Services
Specializing in vacuum casting services and CNC machining, WayKen provides an efficient and cost-effective solution for prototyping and low-volume production. Whether in aerospace, medical devices, consumer products, or beyond, we offer comprehensive expertise to turn conceptual designs into functional prototypes and end-use parts.
WayKen also commits to delivering projects within tight deadlines, focusing on rapid turnaround times without ever compromising on quality. Choosing us for your vacuum casting projects guarantees products of exceptional quality.
Conclusion
One economical way to create intricate rubber and plastic parts in small quantities is through vacuum casting. When testing a product throughout its development phase, product teams frequently utilize vacuum-cast components. Silicone vacuum casting is an affordable manufacturing solution with outstanding performance, offering a vast array of applications.
FAQs
How much does vacuum casting cost?
For producing small batches of parts (between 10 and 50), vacuum casting is an affordable technique. You should typically budget between $200 and $1000 for the mold, with individual units costing around $10 to $100. Nonetheless, the cost can vary significantly depending on the type, scope, and complexity of your project.
Can vacuum casting be used for large-scale production?
Due to the manual effort required and the slower production rates compared to other technologies such as injection molding, vacuum casting is less economically viable for large-scale production, even if it is highly efficient for making small to medium-sized batches.
Is vacuum casting suitable for complex designs?
Yes, vacuum casting works exceptionally well for intricate shapes. Complex geometries and intricate features that can be challenging or expensive to produce with conventional manufacturing techniques can be replicated with silicone molds.






