- September 9, 2022
Modern product manufacturing requires processes and techniques that ensure precision and accuracy due to the increasing complexity of product design. Consequently, there is a rush for development and innovation in manufacturing techniques, especially the introduction of automation.
Due to automation, CNC machining is a common manufacturing process known for its precision, accuracy, and capability for complex product design. This article will discuss CNC machining basics, its process, application, and benefits.
What Does Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Mean?
Computer numerical control (CNC) involves controlling a machine tool using a microcomputer attached to the tool. The microcomputer can do this by responding to a programming language called G-code and M-code, which contains instructions on machining parameters such as feed rate, spindle speed, cutting tool, and coolant flow.
The microcomputer then relays the instructions to the machine tool. Therefore, CNC machining does not require manual operation, making it suitable for creating error-free parts irrespective of the complexity of the product design.
What is CNC Machining?
CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that involves removing part of a workpiece using instructions from a CAD model to make a product. The CNC machine removes parts of the workpiece by machining operations such as turning, drilling, or milling, according to codes (g-code and m-code) obtained from the CAD model and containing instructions on machining parameters.
CNC machining process is compatible with many metals, plastics, wood, and composite materials. Alongside the additive and formative manufacturing processes, like 3D printing, and injection molding, it forms a go-to staple process for part manufacturing. However, CNC machining has some advantages over these methods, such as high tolerance. Let’s keeping reading.
4 Main Steps for CNC Machining Process
There are four basic steps to CNC machining, no matter your CNC machining process. Below is a stepwise procedure on how they generally function:
Step 1: Prepare a CAD Model
This involves creating a 2D or 3D model design of the product. There is much software suitable for the process, with popular ones being AutoCAD and SolidWorks. Furthermore, it is possible to convert 2D designs to 3D designs depending on the product requirement.
Although some product designs might be simple, preparing some CAD models might require advanced knowledge, especially complex product designs.
The CAD model should be properly designed and effortlessly show the operator critical features such as tolerance, construction lines, threads, and other parameters for an effective machining operation.
Step 2: Conversion to CNC Compatible Format
CNC machines won’t understand the CAD model. Therefore, you have to transform the CAD model to a CNC-compatible format so that the machine can interpret it. For this step, you can use CAM software such as AutoCAD, Fusion 360, or other online software services.
This software can convert to a CNC-compatible format and will instruct the CNC machine on parameters. Such as rotational and linear movement, cutting sequence, toolpath, workpiece, machine speed, etc., associated with the machining operation.

Step 3: Setup Execution
This involves choosing the right type of CNC machine and configuring certain operations before the machining operation begins. Selecting the right machine depends on the workpiece, the complexity of product design, and the cost. Afterward, the workpiece is mounted on the machine.
Step 4: Machine the Part
The operator will attach the necessary cutting tools and kickstart the process. The process is automated and will run until deemed complete by the computer program. During and after the machining process, machinists will do several levels of inspection to occur for quality assurance.
The Important Role of Machinists in CNC Machining
Even though the CNC machining process is automated, there are CNC machinists to cater to anticipated and unanticipated faults. Below are the important roles of CNC machinists:
- Find product specifications.
- Read blueprints, sketches, and CAD/CAM files.
- Create CAE models.
- Align and adjust cutting tools and other machine materials.
- Install, use, and disassemble CNC machine tools.
- Observe the machine’s speed.
- Inspect and test finished products for flaws.
- Ensure that a part is aligned to the CAD model.
Types of CNC Machines
Each CNC machining process has its machine. For example, machines for CNC milling are called CNC milling machines, and those for CNC turning are called CNC lathes. However, the type of CNC machines is more of the axis at which they can move and rotate. Here are the common ones used in part manufacturing:
2-Axis CNC machines
2-axis CNC machines can machine a part only on the x and z axes, i.e., vertically and horizontally. Therefore, they are the simplest CNC machine used in part manufacturing.

3-Axis CNC machine
3-axis CNC machines take a further step ahead of the 2-axis CNC machine as they can move in the x, y, and z axes. They are the commonest machines used in CNC machining. However, there can be a limitation in the ability to machine parts with complex designs. This is due to their lack of rotation.
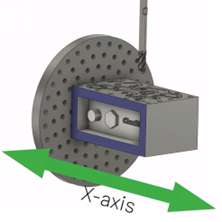
4-Axis CNC machines
The 4-axis CNC machine has a spindle that can travel along the three axes. In simple terms, the machine can go up and down, side to side, back and forth, and rotate along the X and A axes. All this happens without the workpiece moves. They are the most common CNC machines used in machining complex parts due to their speed, precision, and accuracy.

5-Axis CNC machines
A 5-axis CNC machine has a spindle and cutting tool that can move similarly to the 4-axis machine. However, unlike the 4-axis machine, they can rotate along any two of the three axes. They are considered the most complete multi-axis CNC machine due to their ability to approach the workpiece from all directions without manual repositioning during machining. 5-axis CNC machining enables perfect operations of precision and complex parts
3 Common Support Softwares for CNC Machining
Depending on the CNC machining process requirement, every machining uses one or more of the software listed below:
1. CAD Software
CAD software allows the operator to produce 2D and 3D models of physical components used in product design and manufacturing. Aside from that, they function in providing design data to manufacturers. Examples include AutoCAD (2D and 3D), Inventor (3D), Blender, and SketchUp.
2. CAM Software
CAM software is suitable for creating G-codes from CAD models for those controls CNC machines. Consequently, a CNC machine has automation. Top examples include Fusion 360, SolidWorks, and AutoCAD.
3. CAE Software
CAE software allows product designers to mimic the performance of an intended product. Consequently, they can enhance product designs and helps engineers solve engineering-related issues. Examples include finite element analysis, multibody dynamics, and computational fluid dynamics.
Different Types of CNC Machining Operations
CNC machining comprises several techniques involving subtractive removal of part of a workpiece to make the intended product. However, the style of removal depends on the process. Common CNC machining operations used in part manufacturing include:
CNC Drilling
CNC drilling involves using a rotating cutting tool to create cylindrical holes in a stationary workpiece. It is an important CNC machining operation used in making products that need part assembly.
CNC Milling
CNC milling is the most common machining operation that involves using a cutting tool that can rotate and move along axes to remove material from a workpiece. The ease of cutting depends on the sophistication of the CNC machine.

CNC Turning
CNC turning is a machining operation that involves rotating a product while feeding it to a cutting tool produced to make the machined part.
Others Machining Operations
- Grinding
- Broaching
- Lapping
- Sawing
- Honing
Materials Compatible with CNC Machining
–Metals: copper, stainless steel alloys, titanium, brass, aluminum alloys, steel, magnesium, etc.
–Plastics: acetal, PEEK, polycarbonate, nylon, acrylic, PVC, polypropylene, etc.
–Composite: epoxy, phenolics, fiberglass, and carbon fiber.
–Wood: hardwood and plywood.
–Foam: rigid and carving foam.
CNC machining is compatible with many materials. However, before choosing a CNC material, consider the following:
- Hardness
- Mechanical properties
- Part functions
- Dimensional Tolerance
- Operating Temperature
- Cost
What are the Benefits of CNC Machining?
CNC machining has wide applications in industrial part manufacturing due to several advantages. Below are a few benefits of the process over other manufacturing operations.
Accuracy and Precision
CNC machining is accurate, allowing product manufacturers to make parts according to the intended design. Aside from that, it has high precision and tolerance; therefore, you can manufacture different batches of a product without losing accuracy. Furthermore, being an automated process reduces the errors during machining.
Fast and Efficient
You can get a CNC machined part in a few days. Therefore, it is production efficiency. However, the speed and efficiency depend on the type of CNC machine and the complexity of the product.
Cost-effectiveness
CNC machining has a high initial investment cost. However, it has a lower operational cost. Aside from that, the high output rate, little or no human error, and low production cost increase its cost-effectiveness. In addition, for most machining operations, less training is required, and training is most available online.
Better Capabilities
Most CNC machines can carry many tools for different purposes. Aside from that, they have sophisticated software that allows them to work on different products and complex workpieces. Therefore, they have enhanced capabilities and compatibility with workpieces of different sizes, shapes, or textures.
Wide Range of Compatible Materials
Machining operations are compatible with a large base of materials. Common examples are metal, plastic, and composite.
Alternative Manufacturing Processes to CNC Machining
CNC machining is a versatile process widely accepted in part and product manufacturing. However, sometimes it might not be the best method. Here are several alternative methods that you can consider:
3D Printing
3D printing is an additive manufacturing process that involves melting, depositing, and solidifying a material using instructions from a CAD or digital 3D model. Like CNC machining, it is automated. However, unlike CNC machining, it is more suitable for a simple design.
Injection Molding
Injection molding is a plastic manufacturing process that involves melting and injecting material into a prepared mold and letting it solidify. It operates using the same mechanism as other manufacturing processes, such as blow molding, overmolding, and insert molding. It is an important part of the mass fabrication of products.
Die Casting
Die casting is similar to injection molding. However, it is suitable for metals such as aluminum. It involves melting the metal and injecting it into a prepared mold. The injection method can be low or high, depending on the product’s quality.
A Brief History of CNC Machining
Before the electronic age, designers created parts by hand or by manually operated machines. The manufacturing processes used at this stage are limited in accuracy, precision, suitability for complex products, and, most importantly, mass production of products. As a result, there were research and development into introducing new manufacturing processes.
The first glimpse into numerical control was when John T. Parsons, in collaboration with MIT, developed the numerical control machines in part manufacturing in the US Airforce in the 1940s. These machines allow manufacturers to control a set of tools using instructions from punch cards. However, they still lack whole automation. Consequently, they were used with operators present.
With the invention of faster computers, the CNC machine started using digital codes instead of punch cards to control the machine tools. CNC machining can produce parts more quickly and accurately than the previous machining system.
Conclusion
CNC machining is a widely accepted set of processes in part and product manufacturing due to its accuracy, precision, and tolerance. Therefore, making it easy for product designers and manufacturers to create products of different complexity.
Are you looking for high-quality CNC machined parts? Then, get services at WayKen and make access to quality at a competitive price.
FAQs
What are M-code and G-code?
On the one hand, G-codes are a set of codes that instruct a CNC machine on how to move. On the other hand, M-code carries out the machine’s non-cutting operations.
What are the main challenges in CNC machining?
Customization is not particularly easy with CNC machining. Machinists must modify the CAD files in the initial step to make minor adjustments to the finished products. Also, technological improvement allows only a skilled operator to write the programs.
What industries are CNC machining used in?
CNC machining has applications in many manufacturing industries. Common industries adopting the manufacturing process include automotive, aerospace, military, defense, marine, and medical.
What are the terminologies in CNC machining?
Common terminologies in CNC machining include:
-CAD: Computer-Aided Software
-CAM: Computer-Aided Manufacturing
-CAE: Computer-Aided Engineering
-DNC: Distributed Numerical Control
-G-code: Geometric Codes
-M-code: Miscellaneous Machine Codes
What are the trends in the CNC machining industry?
The trends in the CNC machining industry include full automation of the procedure, adding more axes to CNC machines, and developing more features for easy customization.